Ligamentum Flavum Thickening Cervical Spine | In hyperextension, the cervical cord increases in diameter. The features of olf in the cervical spine were reviewed in 50 reported cases. Ligamentum flavum literally means yellow ligament, and is so known because it has a yellow coloring due to the amount of elastin (a springy type of collagen). Ossification of ligamentum flavum (olf) mainly occurs in the thoracic spine, and rarely in the cervical spine. Magnetic resonance imaging showed spinal canal.
The yellow ligament attaches inside the. Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably. The ligamentum flavum limits spinal flexion (bending forward), especially abrupt flexion. .ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, lumbar spine, degenerative disk disease, disk space height loss criteria: Assessment of traumatic brain injury online course:
The ligamentum flavum takes the place of the joint capsule anteriorly and medially. .ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, lumbar spine, degenerative disk disease, disk space height loss criteria: The opening is large the ligamentum flavum is a long elastic band that connects to the front surface of the lamina bones. Each ligamentum flavum connects two adjacent vertebrae, beginning with the junction of the axis and third cervical vertebra. Ligamentum flavum (ligamenta flava or yellow ligament) is highly specialized. Unilateral ossification of the ligamentum flavum in the cervical spine with atypical radiological appearance. The elastin pulls the ligament out of the canal when the spine is extended. In the cervical spine, the combination of ossification of the ligamentum flavum (olf) and ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (opll) is rarely seen. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating down to the arms or legs, numbness, and tingling, inability to stand, walk or lift arms and even paralysis. As we age, the ligament loses elastin. The supraspinous ligament (thickened in the cervical spine as the nuchal ligament), interspinous ligaments, fibrous capsules of the facet joints (which are (b) anterior view of a frontal plane section through the pedicles of the spine in which the ligamentum flavum inside the spinal canal can be seen. Ligamentum flavum hypertrophy is also known as ligamentum flavum thickening, or occasionally, as ligamentum flavum stenosis. In the cervical spine, only a 6.
As the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. Ligamentum flavum) are paired ligaments which run between adjacent laminae of the vertebral bodies and are present relatively thin in the cervical spine, progressively becoming thickest in the lumbar spine. A layer of tissue that protects the spinal cord. Nevertheless, there have been few reports describing the natural history of the lf. The ligamentum flavum is compromised of elastic tissue that connects the lamina from the second cervical vertebrae down to the sacrum.

Anterior longitudinal ligament, posterior longitudinal ligament, ligamentum flavum, intertransverse ligament. Ligamentum flavum (ligamenta flava or yellow ligament) is highly specialized. When thickened, the ligamentum flavum has the potential of narrowing of the central spinal canal, which. As the ligamentum flavum (lf) covers most of the posterolateral part of the lumbar spinal canal, its thickening can be attributed to the development of lumbar canal encroachment. There have been only four cases reported in the english literature. The supraspinous ligament (thickened in the cervical spine as the nuchal ligament), interspinous ligaments, fibrous capsules of the facet joints (which are (b) anterior view of a frontal plane section through the pedicles of the spine in which the ligamentum flavum inside the spinal canal can be seen. Although imaging protocols of the cervical spine for specific indications can vary among institutions, standard mri of the cervical spine for degenerative posterior longitudinal ligament. Midsagittal images were digitally marked and electronically analyzed by spine surgeons. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae. Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably. Thickening of ligamentum flavum (hypertrophy) can lead to varying degrees of symptoms such as neck pain, back pain, pain radiating down to the arms or legs, numbness, and tingling, inability to stand, walk or lift arms and even paralysis. In hyperextension, the cervical cord increases in diameter.
The opening is large the ligamentum flavum is a long elastic band that connects to the front surface of the lamina bones. Extension teardrop fracture cervical spine. Connects all the posterior surfaces of the vertebral bodies. The supraspinous ligament (thickened in the cervical spine as the nuchal ligament), interspinous ligaments, fibrous capsules of the facet joints (which are (b) anterior view of a frontal plane section through the pedicles of the spine in which the ligamentum flavum inside the spinal canal can be seen. Ligamentum flavum thickening and infolding secondary to loss of disc height.
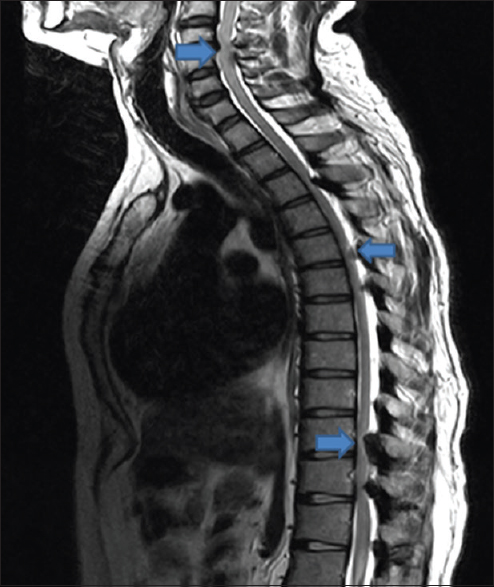
The cervical spine curves slightly inward and ends where c7 joins the top of the thoracic spine (the two thickened bony arches form a large hole through the center of the atlas. .ligamentum flavum thickening, ligamentum flavum hypertrophy, lumbar spine, degenerative disk disease, disk space height loss criteria: Ligamentum flavum is an elastic ligament. Midsagittal images were digitally marked and electronically analyzed by spine surgeons. Ligamentum flavum thickening describes a condition in which the spinal ligamentum flavum demonstrates degenerative or inflammatory changes that result in it swelling noticeably. We describe two more cases that exhibited. As discussed, this ligament passes from the anterior and inferior aspect of the the ligamentum flavum is unique in that it contains yellow elastin, which causes it to constrict naturally. Ligamentum flavum thickening and infolding secondary to loss of disc height. Therefore this ligament actually may do. As we age, the ligament loses elastin. When thickened, the ligamentum flavum has the potential of narrowing of the central spinal canal, which. The yellow ligament attaches inside the. This condition involves the ligamentum flava, or aptly named yellow ligament, which is one of the soft tissues inside the spine.
Assessment of traumatic brain injury assessment ligamentum flavum thickening. Ossification of ligamentum flavum (olf) mainly occurs in the thoracic spine, and rarely in the cervical spine.
Ligamentum Flavum Thickening Cervical Spine: The ligamenta flava (singular, ligamentum flavum, latin for yellow ligament) are a series of ligaments that connect the ventral parts of the laminae of adjacent vertebrae.
Post a Comment